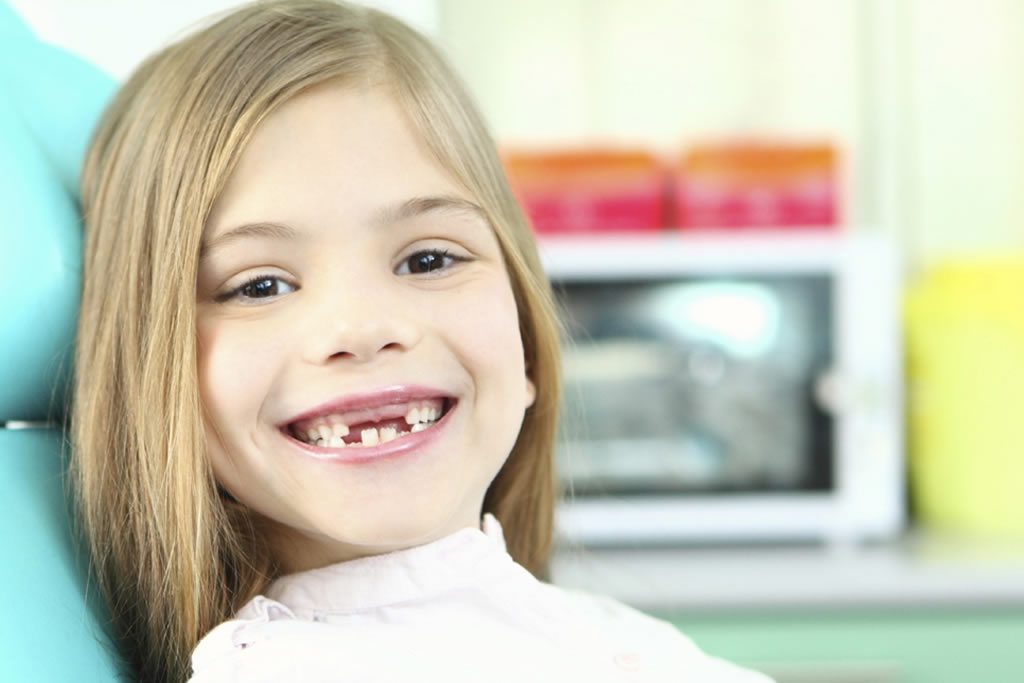

We believe it is a privilege to treat children and that we have a wonderful opportunity to make a difference in their lives. We are committed to oral health for infants, children and those with special needs. Our mission is to ensure that each child and family receive respect, support and the finest dental care in a safe and nurturing environment. We believe that every child deserves to have a happy and healthy smile!
Early Treatment
Our practice can provide a wide range of dental services for your children. Our flexibility in our services saves you time and keeps your total dental care within one practice. Our emphasis is on total preventive care for our patients. Total care begins with regular hygiene visits, regular checkups and continued home oral health routines. We provide many preventative measures to keep your child’s teeth clean and healthy, including sealants and fluoride treatments. We also educate the parents in early detection of some common problems children may face, including thumb sucking, bruxism and baby bottle tooth decay.Teething
Normally the first tooth erupts between ages 6 to 12 months. Gums are sore, tender and sometimes irritable until the age of 3. Rubbing sore gums gently with a clean finger, the back of a cold spoon or a cold, wet cloth helps soothe the gums. Teething rings work well, but avoid teething biscuits—they contain sugar that is not good for baby teeth.Infant’s New Teeth
The primary, or “baby,” teeth play a crucial role in dental development. Without them, a child cannot chew food properly and has difficulty speaking clearly.Primary teeth are vital to development of the jaws and for guiding the permanent (secondary) teeth into place when they replace the primary teeth around age 6.
Since primary teeth guide the permanent teeth into place, infants with missing primary teeth or infants who prematurely lose primary teeth may require a space maintainer, a device used to hold the natural space open.
Without a maintainer, the teeth can tilt toward the empty space and cause permanent teeth to come in crooked. Missing teeth should always be mentioned to your family dentist. The way your child cares for his/her primary teeth plays a critical role in how he/she treats the permanent teeth.
Children and adults are equally susceptible to plaque and gum problems—hence, the need for regular care and dental checkups.
A Child’s First Dental Visit
A child’s first dental visit should be scheduled around his/her first birthday. The most important part of the visit is getting to know and becoming comfortable with a doctor and his staff. A pleasant, comfortable first visit builds trust and helps put the child at ease during future dental visits. If possible, allow the child to sit in a parent’s lap in the exam room.Why Primary Teeth Are Important
Primary teeth are important for several reasons:
Foremost, good teeth allow a child to eat and maintain good nutrition. Healthy teeth allow for clear pronunciation and speech habits. The self-image that healthy teeth give a child is immeasurable. Primary teeth also guide eruption of the permanent teeth. Good Diet and Healthy Teeth The teeth, bones and soft tissue of the mouth require a healthy, well-balanced diet. A variety of foods from the five food groups helps minimize (and avoid) cavities and other dental problems. Most snacks that children eat cause cavities, so children should only receive healthy foods like vegetables, low-fat yogurt and cheeses, which promote strong teeth.Infant Tooth Eruption
A child’s teeth actually start forming before birth. As early as 4 months of age, the primary or “baby” teeth push through the gums—the lower central incisors are first, then the upper central incisors. The remainder of the 20 primary teeth typically erupt by age 3, but the place and order varies. Permanent teeth begin eruption around age 6, starting with the first molars and lower central incisors. This process continues until around age 21. Adults have 28 secondary (permanent) teeth—32 including the third molars (wisdom teeth).Preventing Baby Bottle Tooth Decay
Tooth decay in infants can be minimized or totally prevented by not allowing sleeping infants to breast or bottle-feed.Infants that need a bottle to comfortably fall asleep should be given a water-filled bottle or a pacifier.Encourage your child to drink from a cup as they approach their first birthday. He/she should be weaned from the bottle at 12-14 months of age. Let us know if you notice any signs of decay or anything unusual in your child’s mouth.
FAQ’s
How should I clean my baby’s teeth?
A toothbrush with soft bristles and a small head, especially one designed for infants, is the best choice for infants. Brushing at least once a day, at bedtime, will remove plaque bacteria that can lead to decay.When should my child start using toothpaste?
Use a kids fluoridated toothpaste from age 1.Earlier than that, clean your child’s teeth with water and a soft-bristled toothbrush. After age 3, parents should supervise brushing. Use no more than a pea-sized amount of toothpaste and make sure children do not swallow excess toothpaste.How can I help my child through the teething stage?
Sore gums when teeth erupt are part of the normal eruption process. The discomfort is eased for some children by use of a teething biscuit, a piece of toast or a frozen teething ring. Your pharmacy should also have medications that can be rubbed on the gums to reduce the discomfort.If my child gets a cavity in a baby tooth, should it still be filled?
Primary, or “baby,” teeth are important for many reasons. Not only do they help children speak clearly and chew naturally, they also aid in forming a path that permanent teeth can follow when they are ready to erupt. Some of them are necessary until a child is 12 years old or longer.Pain, infection of the gums and jaws, impairment of general health and premature loss of teeth are just a few of the problems that can happen when baby teeth are neglected. Also, because tooth decay is really an infection and will spread, decay on baby teeth can cause decay on permanent teeth.
Proper care of baby teeth is instrumental in enhancing the health of your child.
Can thumbsucking be harmful for my child’s teeth?
Thumb and pacifier sucking habits that go on for a long period of time can create crowded, crooked teeth or bite problems. If they are still sucking their thumbs or fingers when the permanent teeth arrive, a mouth appliance may be recommended by your dentist. These appliances can only be fitted after the age of 6 years which is often too late as the permanent dentition is already affected. Alternatively, you can purchase a thumb guard http://endthumbsucking.com/.
What are dental sealants and how do they work?
Sealants are clear or shaded plastic applied to the teeth to help keep them cavity-free. Sealants fill in the grooved and pitted surfaces of the teeth, which are hard to clean, and shut out food particles that could get caught, causing cavities. Fast and comfortable to apply, sealants can effectively protect teeth for many years.If my child gets a toothache, what should I do?
To comfort your child, rinse his/her mouth with warm salt water and apply a cold compress or ice wrapped in a cloth on your child’s face if it is swollen. Do not put heat or aspirin on the sore area, but you may give the child paracetamol for pain. See us as soon as possible.Is my child getting enough fluoride?
Fluoride has been shown to dramatically decrease a person’s chances of getting cavities by making teeth stronger.Fluoride in the drinking water is the best and easiest way to get it.If your child is not getting enough fluoride internally through water (especially in communities where the water is not fluoridated) or if your child drinks bottled water without fluoride, your dentist may prescribe fluoride supplements.
I noticed a space between my child’s two upper permanent front teeth. Is this cause for concern?
Usually, the space will close in the next few years as the other front teeth erupt. We can determine whether there is cause for concern.My child plays sports. How should I protect my child’s teeth?
A mouth guard should be a top priority on your child’s list of sports equipment. Athletic mouth protectors, or mouth guards, are made of soft plastic and fit comfortably to the shape of the upper teeth.They protect a child’s teeth, lips, cheeks and gums from sports-related injuries. Any mouth guard works better than no mouth guard, but a custom-fitted mouth guard fitted by our doctor is your child’s best protection against sports-related injuries.
